Stratasys 3D printers & materials are behind some of the transportation sector’s biggest success stories.
From horse and cart to space age, the transportation sector has always embraced change, and over the last quarter-century, this questing industry has increasingly turned to the possibilities of additive manufacturing to stay at the cutting edge. From a new passenger rail network to a race car shaving milliseconds off its track time, the potential applications for 3D printing are huge and technology must be several steps ahead of the curve just to keep up. Fortunately, the breadth of Stratasys 3D printers and materials – not to mention the ever-evolving skill-set of the Tri-Tech 3D team – has ensured the demands of the most ambitious transportation sector visionaries are not only met but exceeded.
Which Stratasys 3D printers are often used in transportation?
As you’ll see from the case studies below, transportation can mean anything from supersonic air travel to Super GT racing, so Tri-Tech 3D always weighs up each client’s situation and business objectives rather than taking a ‘one size fits all’ approach. As a very general rule, however, we’ve been impressed by the results that transportation firms have achieved with Stratasys 3D printers including the large-scale-production Fortus 900mc, the super-accurate powder bed fusion H350, Neo series stereolithography models like the Neo 450E, Neo 450S and Neo 800, plus the F450 and factory floor-ready F370CR.
Which 3D printing materials are often used in transportation?
If transportation designers aren’t satisfied by the materials at their fingertips, they’ll go looking elsewhere – and that’s where the open-ended choice of additive manufacturing materials proves invaluable. High-performance PEKK-based thermoplastics like Antero 800NA and Antero 840CN03 excel, while Nylon 6 is great for impact strength and Nylon 12 CF negates the need for metal with its high tensile strength and light weight. Investigate ULTEM 1010 for a rugged thermoplastic with stellar heat resistance, while ABSCF10 is a unique carbon fibre-filled ABS that’s 15% stronger and 50% stiffer than standard. Also, consider strong and versatile photopolymers like PA11 and PA12.
* 9085, 1010, and ULTEM™ are trademarks of SABIC, its affiliates or subsidiaries
Which applications is 3D printing used for in the transportation sector?
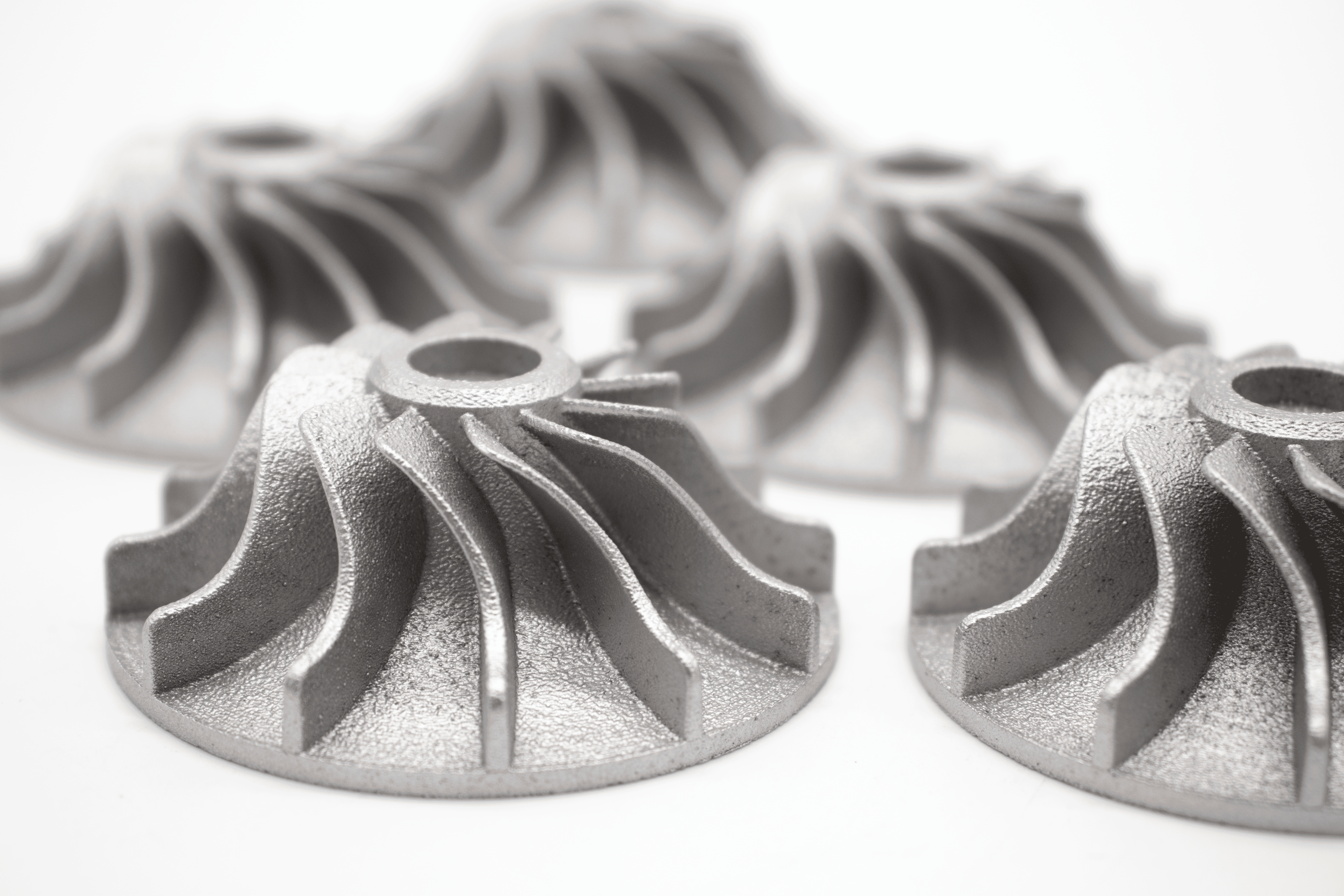
Since the rise of AM in the post-millennium, the transportation sector has moved at rocket pace and 3D print technology has been used for a thousand exciting projects, parts and components that simply wouldn’t have been possible with traditional manufacturing techniques. Working across the sector, we’ve seen common applications that include: composite tooling, greasing jigs, production parts, rapid prototyping, functional prototyping, jigs and fixtures, composite tooling and casting patterns.
What examples are there of Stratasys 3D printers used by the transportation sector?
The world’s most exciting transportation firms turn to Stratasys 3D printers and materials, while tapping the knowledge of Tri-Tech 3D. Nissan’s specialised motorsports team NISMO used the Origin One platform to create elements of the revolutionary GT500 race car, while the UK’s Senior Aerospace BWT installed the Stratasys Fortus 450mc 3D printer to boost the design, production and deployment of interior aircraft parts. The UK’s leading rolling stock provider Angel Trains has used a Fortus 450mc and ULTEM 9085 resin to create the first 3D-printed parts ever deployed inside an operational passenger train, while Denver-based Boom Supersonic edged closer to its ambitious goal of mainstream supersonic air travel using F370 and Fortus 450mc 3D printers.