One Click Metal
Introducing the one-stop solution for metal 3D printing
What is metal 3D printing?
While additive manufacturing (AM) is often associated with components created using next-generation polymers and thermoplastics, many designers and engineers turn to metal 3D printing to benefit from open-ended design flexibility combined with the mechanical advantages that only high-performance metals can provide.
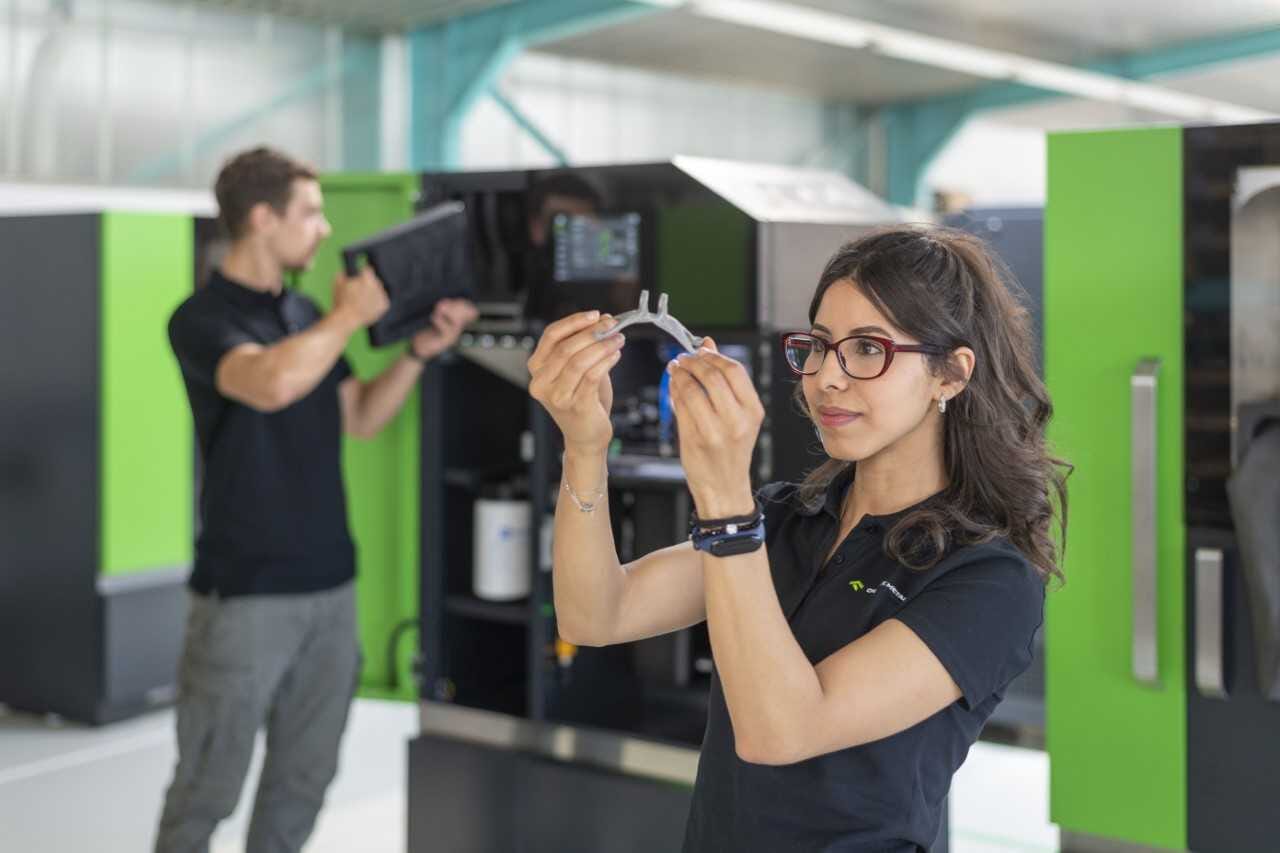
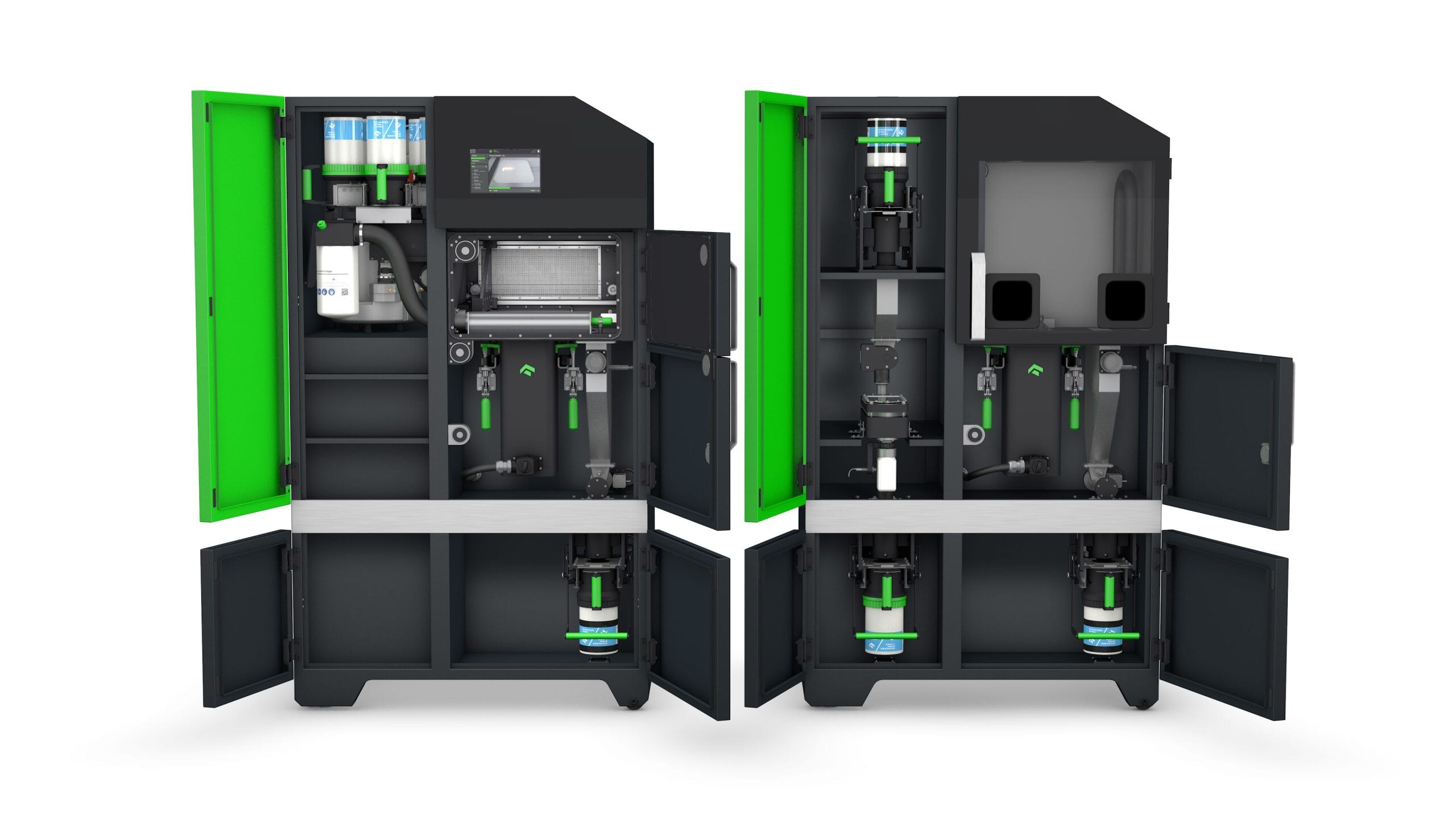
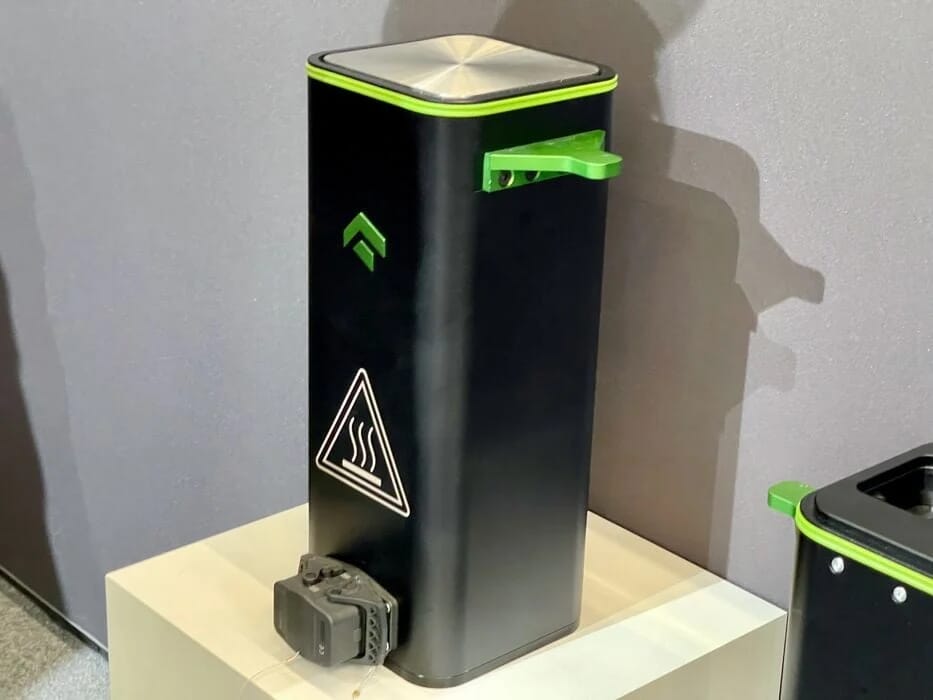
Tri-Tech 3D’s experts are always on-hand to advise you on the best metal 3D printers for your needs, including the class-leading One Click Metal MPRINT. Developed by a team of AM pioneers based near Stuttgart, Germany, this low-cost, laser-based direct metal 3D printer is an excellent choice, potentially leading your project from initial CAD design to final component in the same day, without compromising strength relative to conventional metals.
Here, you’ll find answers to some of the most common questions we are asked by clients, alongside metal 3D printing case studies and all the models in our range.
Metal 3D Printing Benefits
-
Faster time-to-marketBy cutting product development cycles with a streamlined metal 3D printing process, organisations are more agile and generate greater revenue
-
Reduced manufacturing costsMetal 3D printing boosts manufacturing flexibility, letting you optimise your output and produce the most affordable and efficient parts
-
Efficient manufacturing workflowsMetal 3D printed parts let manufacturers become more dynamic and responsive, cutting the time between initial design and final product
-
Ambitious componentryMetal 3D printing supports the design and delivery of geometrically complex parts, allowing ambitious ergonomics with no impact on cost
-
No custom tooling requiredEliminate the need for custom tooling or fixturing setups associated with traditional manufacturing, while reducing overheads and allowing low-volume production runs
-
Simpler design processUnlike traditional machined parts – which demand detailed drawings and/or CAM work – metal 3D printing software automatically generates the required tool paths
-
Is there a 3D printer that uses metal?
Not all 3D printers can print metal directly, so you’ll need a specialist model. There’s an array of dedicated metal 3D printers on the modern market – and at least ten different print processes – but at Tri-Tech 3D, we’ll always direct you towards the best choice of hardware for your application, with the One Click Metal range an excellent starting point, and the XJet series also well worth investigating.
-
What can I make with a metal 3D printer?
The use of metal 3D printing in sectors spanning from aerospace to medicine underlines just how adaptable this AM technology is. Look a little closer and you’ll see metal 3D printing employed in applications including surgical implants, jewellery, end-of-arm tooling and complex bracketry, to name just a few.
-
What is the most common metal 3D printing?
The various technologies and processes associated with metal 3D printing include direct energy deposition, material extrusion, binder jetting, direct metal laser sintering and selective laser sintering. Of these, powder bed fusion – in which a heat source like a laser or thermal print head is used to consolidate powder-form material to create 3D components – is perhaps the most common.
-
How strong is metal 3D printing?
Taking steel as an example, 3D printed metal components can be at least as strong as their traditional machined counterparts (in fact, in many cases, AM-created parts are even stronger, thanks to the technology’s ability to create lattice infills). To give another example, a component produced using laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) will typically beat the strength of an equivalent casted part, due to the higher density and lower chance of internal voids.
-
Can you 3D print titanium?
Titanium is a popular material associated with 3D metal printing, most commonly used alongside technologies like direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) and selective laser sintering (SLS). But that’s just one of a wide range of feasible materials, including (stainless) steel, aluminium, copper, cobalt, tungsten, nickel-based alloys, platinum, gold and silver.
-
Are metal 3D printers worth it?
At a glance, the metal 3D printing process can seem more expensive due to the relative cost of materials and the longer build times than some AM disciplines. But for low-to-medium volume production, metal 3D printing is cost-effective and delivers high-quality results – giving your business a potentially priceless edge.
What are common applications for One Click Metal printers?
New to 3D
Printing or looking
for some support?
- Call: 01782 814551
- Email: info@tritech3d.co.uk