If you’ve ever wondered what materials can be 3D printed, or what material does a 3D printer use, read this introductory blog from Tri-Tech 3D’s experts
Two of the most common questions we’re asked by clients taking first steps into Additive Manufacturing are ‘What materials can be 3D printed?’ and ‘What material does a 3D printer use?’ It’s testament to just how adaptable 3D printing is that our answer can be pretty long! After all, one of the key benefits of AM is the almost limitless array of materials you can load into a Stratasys 3D printer, and the equally diverse properties of the objects taking shape in the print bed.
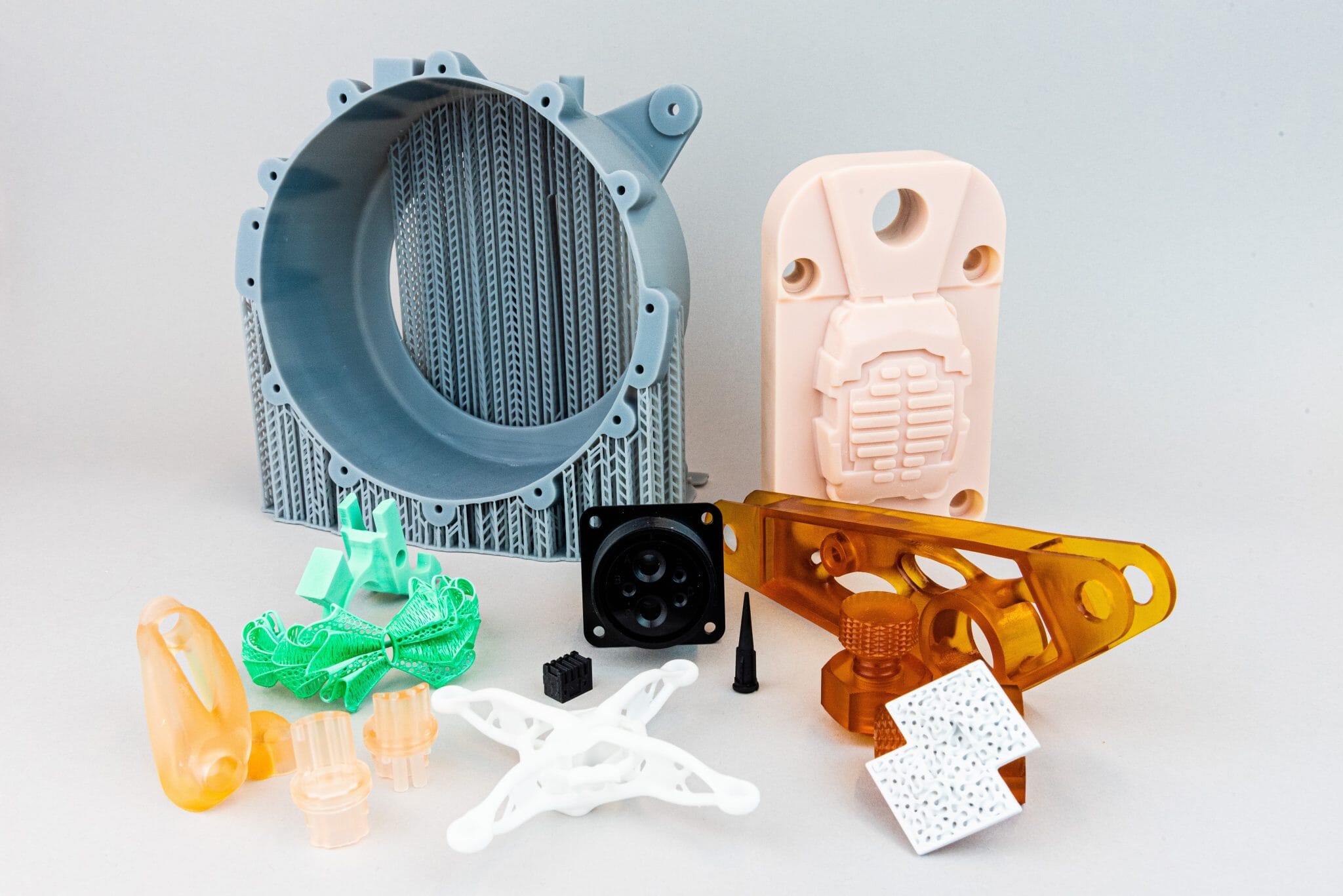
The potential materials for use in 3D printing span from revolutionary filaments to game-changing metal powders – and the choice can be head-spinning. To keep things simple, in this blog, we’ll introduce you to the four most common groups of materials for 3D printing, with benefits and potential uses for each.
Thermoplastics
The term ‘thermoplastic’ refers to a polymer-based material that is solid at room temperature, becomes soft and pliable when heated, then reverts to its original consistency upon cooling. There’s a huge range of thermoplastics available – including ABS, polycarbonates, a variety of blends and a growing selection of engineered materials – and that explains why you’ll find these used in sectors from automotive to aerospace.
From high-strength Nylon CF-10 to high-performance Antero 800NA, every thermoplastic has its own unique properties – and the Tri-Tech 3D team will be glad to guide you through our latest range and suggest the optimum material for individual applications. Meanwhile, some of the general benefits of thermoplastics include:
- Consistent long-term performance
- Low cost
- Variety of colours (or transparent)
- Easy to extrude through nozzle heads
Photopolymers
Starting out as a liquid resin – then hardening when exposed to UV light during AM processes like Stereolithography (SLA) and Digital Light Processing (DLP) – photopolymers are now a hugely popular choice for applications across the gamut of global industry.
The speed of 3D printing objects this way means photopolymers are often used for prototyping. But it’s the massive scope for customisation that makes these materials such an attractive choice. By blending together a handful of base resins, you can generate around 1,000 composite materials, dialling in every last parameter so the result is tailor-made for your project.
From high-accuracy dental modelling resins like VeroDent PureWhite to heat-resistant DSM Somos® PerFORM Reflect, the Tri-Tech 3D team can talk you through our photopolymer range. However, some general benefits include:
- Rapid print speed
- High accuracy (even for complex geometries)
- Open-ended material customisation
- Smooth finish
Metal Powders
Some clients are surprised to learn that 3D objects can be printed from metal – typically using Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) or Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) – and all are stunned by the huge selection of metal powders out there. From familiar metals like (stainless) steel, titanium, copper, aluminium, cobalt chrome and tungsten, to precious metals including silver, gold and platinum, there’s no shortage of materials to create enviably tough 3D printed objects.
From corrosion-resistant OCM Stainless Steel 17-4PH to the i-ProMelt Dental Metal Powder that excels at complex frameworks, the Tri-Tech 3D team is always on-hand to give individual-led guidance on our exhaustive range of high-performance metal powders. However, the more general benefits include:
- High strength and durability
- Intricate geometries
- Reduced material waste
- Flexible customisation
Ceramics
They’ve been dubbed ‘the material of the future’ by some of AM’s greatest thought leaders – and faced with the growing range of advanced engineering ceramics now available, it’s hard to argue.
When it comes to our own acclaimed range of ceramics – including chemical-resistant C808 Zirconia and temperature-resistant C700 Alumina – finish quality is king. When used alongside NanoParticle Jetting technology (NPJ), these materials can produce objects with unparalleled detail, unbeatably smooth surfaces and high accuracy, even for the most complex geometries. Some other benefits include:
- Design flexibility
- Customisation
- Reduced waste
- Strength and durability
Ask Tri-Tech 3D about 3D printing materials and more.
Tri-Tech 3D is the UK’s most respected voice in AM, helping clients in every sector harness the full potential of this technology. From our choice of Stratasys 3D printers to guidance on materials, software and 3D printer training, Tri-Tech 3D offers the complete AM solution.
To find out more about 3D printing materials, or any other element of AM, get in touch with the Tri-Tech 3D team. We’re ready to assist you on 01782 814551 or info@tritech3d.co.uk